SWMM Hydrology
You can use the Explicit (SWMM 5.1.*) engine in Drainage and Utilities V8i to route flows through the system. However, in order to use SWMM hydraulics, you must load the model through inflows at nodes, or you must select EPA-SWMM Runoff as the runoff method for a catchment. If you are not familiar with SWMM hydrology, we strongly recommend that you read SWMM 5 documentation for a detailed discussion of the topic.
The overall process through which precipitation is converted to flow in conduits and channels is summarized in the following figure.
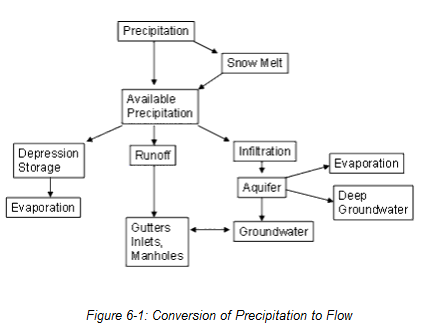
Conversion of Precipitation to Flow
The parameters used in determining runoff can be divided into two categories:
Parameters that are shared by the SWMM model and the Drainage and Utilities native hydrology calculations. These include SCS runoff curve number, Horton max and min infiltration rates, etc. You can enter these parameters in the Property Editor or in the FlexTable for a specific catchment.
Parameters that are unique to the SWMM model. These include evaporation rates, aquifer conductivity, and wilting point. To enter these parameters, you must select Components > SWMM Extensions, then select the appropriate SWMM dialog.
The SWMM engine allows for two different modes when applying the Horton infiltration method when using the EPA SWMM runoff method on catchments:
- Horton - When this method is selected, the precipitation rate is always assumed to exceed the infiltration rate, regardless of how much rainfall as actually infiltrated. Hence the infiltration rate is purely a function of time.
- Horton (Modified) - When this method is selected, infiltration rate is a function of the total amount of rainfall which has infiltrated
You select which method is applied in the calculation property, "Default Infiltration Method" under the "Calculation Options (SWMM Hydrology)".
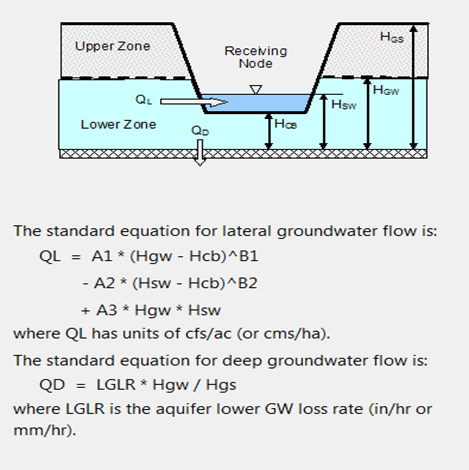
The Groundwater calculation is invoked when the Apply groundwater is set as true in the property of a Subcatchment. It is used to link a subcatchment to both a parent aquifer and to a node of the conveyance system that exchanges groundwater with the subcatchment. It also specifies coefficients that determine the rate of groundwater flow between the aquifer and the node. These coefficients (A1, A2, B1, B2, and A3) appear in the following equation that computes groundwater flow as a function of groundwater and surface water levels.
In addition to the standard flow equation, the solver allows user to define a custom equation whose results will be added onto those of the standard equation. Finally, the dialog offers the option to override certain parameters that were specified for the aquifer to which the subcatchment belongs. The properties listed in the editor are as follows:
- Aquifer Name: Name of the aquifer object that describes the subsurface soil properties, thickness, and initial conditions. Leave this field blank if you want the subcatchment not to generate any groundwater flow.
- Receiving Node: Name of the node that receives groundwater from the subcatchment.
- Surface Elevation: Elevation of the subcatchment's ground surface (ft or m).
- Groundwater Flow Exponent: Value of A1 in the groundwater flow formula.
- Surface Water Flow Coefficient: Value of A2 in the groundwater flow formula.
- Surface Water Flow Exponent: Value of B2 in the groundwater flow formula.
- Surface-GW Interaction Coefficient: Value of A3 in the groundwater flow formula.
- Surface Water Height: Fixed height of surface water at the receiving node above the aquifer bottom (ft or m). Set to zero if surface water depth will vary as computed by flow routing.
- Channel Bottom Height: Water table height above the aquifer bottom that must be reached before any flow occurs (feet or meters). Leave blank to use the receiving node's invert elevation.
- Bottom Elevation: Elevation of the bottom of the aquifer (ft or m). Leave blank to use the value from the parent aquifer.
- Water Table Elevation: Elevation of the water table in the aquifer at the start of the simulation (ft or m). Leave blank to use the value from the parent aquifer.
- Unsaturated Zone Moisture: Moisture content of the unsaturated upper zone of the aquifer at the start of the simulation (volumetric fraction). Leave blank to use the value from the parent aquifer.
- Custom Groundwater Flow Equation: Click the ellipsis button (or press Enter) to launch the Custom Groundwater Flow Equation editor. The equation supplied by this editor will be used in addition to the standard equation to compute groundwater outflow from the subcatchment. The coefficients supplied to the groundwater flow equations must be in units that are consistent with the groundwater flow units, which can either be cfs/acre for US units or cms/ha for SI units.